A highly symbolic, highly effective advertisement by Grumman aircraft, specifically focusing on production of the F6F Hellcat fighter plane.
The emblem of the 7th War Loan would place the date at somewhere after May 7, 1945.
Before NCR was “NCR”, the company was appropriately known as the National Cash Register Corporation. After having been acquired by ATT in 1991, a 1996 restructuring of that firm led to the spin-off Lucent Technologies and NCR, with the firm being the only “spun-off” company that has retained its name.
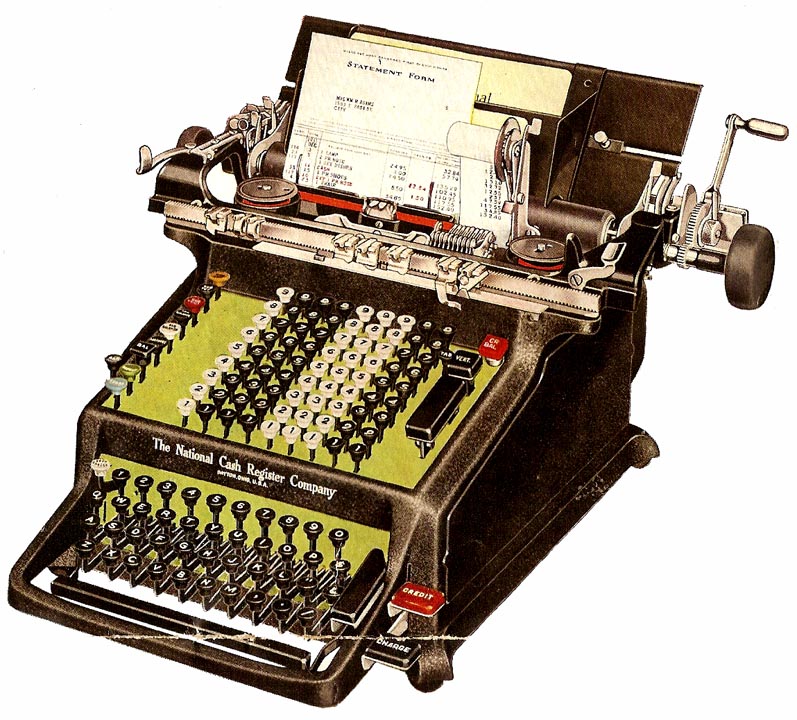
This advertisement, from August 9, 1943, illustrates the company’s National Class 3000 Bookkeeping Machine.
The advertisement is quite simple in style and design. A sketch of a model using an NC 3000 is repeated four times in the same illustration, giving an impression of “depth” and activity as in – well, quite appropriately! – an office setting. An example of a neatly completed bill appears in the background.
The full text of the advertisement appears at bottom. Note the use of alpha-numeric telephone number prefixes (“CIrcle”, “MOtt”, and “CAnal”).
 Here’s an illustration of an NC 3000 from the Office Museum website:
Here’s an illustration of an NC 3000 from the Office Museum website:
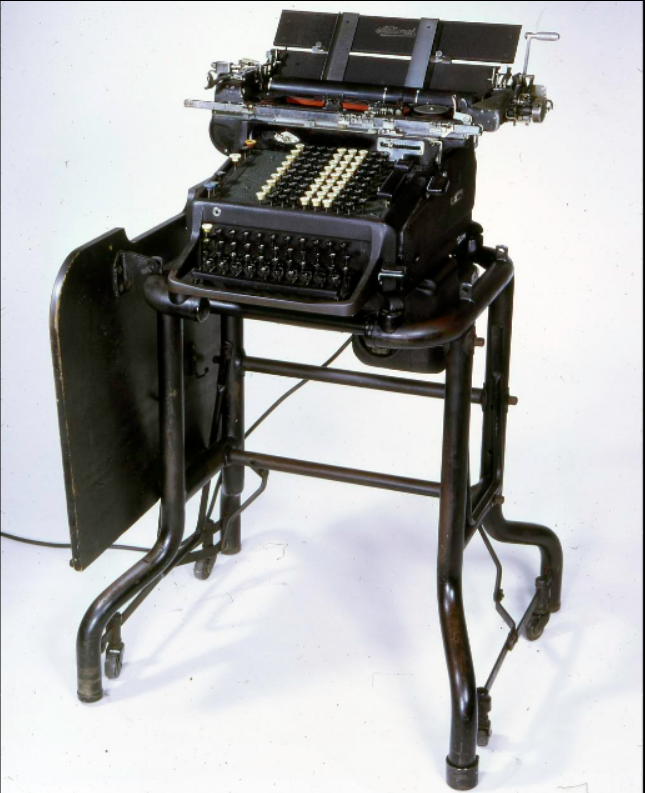
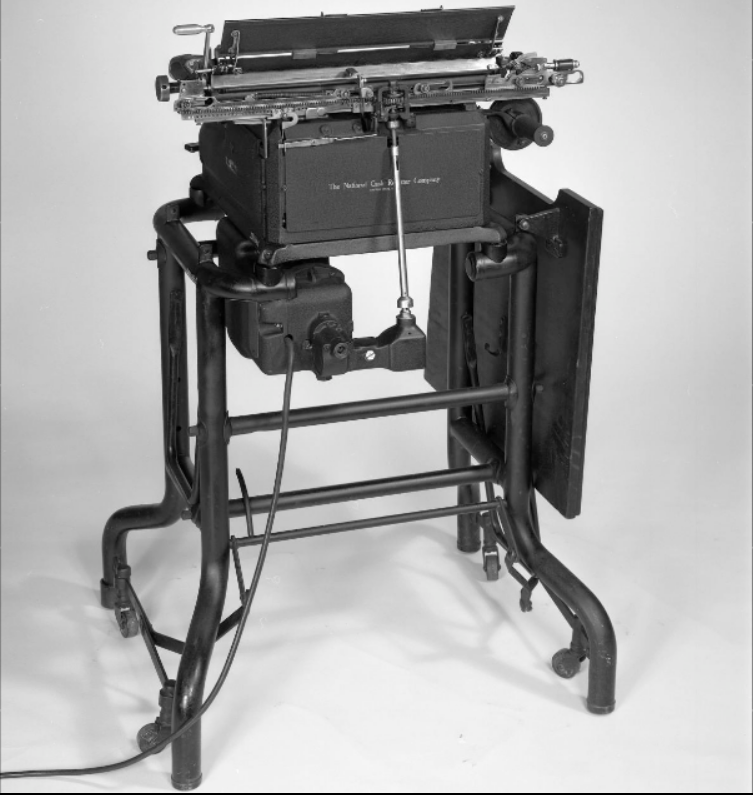
 These two images – showing the front and rear of an NC 3000, on its stand – are from the Smithsonian’s Museum of American History website. This example was manufactured in 1938 or 1939.
These two images – showing the front and rear of an NC 3000, on its stand – are from the Smithsonian’s Museum of American History website. This example was manufactured in 1938 or 1939.
 Without machines to help them do this job, hundreds upon thousands of new bookkeepers would be needed to keep our records, and millions of man-hours would be stolen from our war effort.
Without machines to help them do this job, hundreds upon thousands of new bookkeepers would be needed to keep our records, and millions of man-hours would be stolen from our war effort.
National Typewriting-Bookkeeping Machines in industry, in business and in government are speeding record making and record keeping for the nation because they are simple and easy to operate…for they alone combine the standard adding machine and typewriter keyboards with full visibility of forms in the machines… Any typist with a knowledge of an adding machine becomes a proficient operator with a few hours’ practice.
Nationals are flexible…for they can be changed to do all sorts of bookkeeping…like the statement you receive from the department store or the wholesaler…or for purchase records…payroll writing…posting general ledgers…and numerous other applications.
National Typewriting-Bookkeeping Machines, as well as all other National products and systems, save man-hours and provide protection over money and records for the bookkeeping of the nation.
National Accounting-Bookkeeping Machines may be secured by essential industries through priorities… A stock of modern used National Cash Registers is also available for business needs.
The National Cash Register Company
CASH REGISTERS * ACCOUNTING – BOOKKEEPING MACHINES
40 ROCKEFELLER PLAZA, CIrcle 5-6300
321 EAST 149TH STREET, MOtt Haven 9-3323
138 BOWERY, CAnal 6-4906
References
Early Office Museum – Antique Special Purpose Typewriters, at http://www.officemuseum.com/typewriters_office_special.htm
Mathematical Treasure: National Class 3000 Bookkeeping Machine on Stand, at http://americanhistory.si.edu/collections/search/object/nmah_694189
NCR Corporation, at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NCR_Corporation
National Museum of American History – Bookkeeping Machines, at http://americanhistory.si.edu/collections/object-groups/bookkeeping-machines/national
On March 14, 1945, a few months prior to their advertisement promoting “Plastic” in both military and civilian contexts, GE ran an advertisement – with a similar 6-section graphic and textual design – presenting and explaining the economic, technical, and cultural aspects of “Television” for the postwar world.
In light of the world of 2017, there’s something almost quaint about the the content of and mindset behind this advertisement, exemplified by the description of the kind of programming that was expected to be available: studio stage shows; movies; sports events; news. This was a natural reflection of the entertainment and informational “material” then available to the public, much already extant on radio. Understandably, the ad’s writers could not have foreseen the technological, cultural, and economic changes that – acting in synergy – would sweep the world in the ensuing decades, and continue to do so now. In their lack of knowledge about the future of entertainment, perhaps the copy-writers were fortunate.
An example, perhaps, of the way that the manifestation and anticipated use of any new technology, is – at the time of the introduction of that technology – seen in the immediate intellectual context of that time itself.
 Q. What will sets cost after the war?
Q. What will sets cost after the war?
A. It is expected that set prices will begin around $200, unless there are unforeseen changes in manufacturing costs. Higher priced models will also receive regular radio programs, and in addition FM and international shortwave programs. Perhaps larger and more expensive sets will include built-in phonographs with automatic record changers.
Q. How big will television pictures be?
A. Even small television sets will probably have screen about 8 by 10 inches. (That’s as big as the finest of pre-war sets.) In more expensive television sets, screens will be as large as 18 by 24 inches. Some sets may project pictures on the wall like home movies. Naturally, pictures will be even clearer than those produced by pre-war sets.
Q. What kind of shows will we see?
A. All kinds. For example: (1) Studio stage shows – dancers, vaudeville, plays, opera, musicians, famous people. (2) Movies – any moving picture can be broadcast to you by television. (3) On-the-spot pick-up of sports events, parades, news happenings. G.E. has already produced over 900 television shows over its station, WRGB, in Schenectady.
Q. Where can television be seen now?
A. Nine television stations are operating today – in Chicago, Los Angeles, New York, Philadelphia, and Schenectady. Twenty-two million people – about one-fifth of all who enjoy electric service – live in areas served by these stations. Applications for more than 80 new television stations have been filed with the Federal Communications Commission.
Q. Will there be television networks?
A. Because television waves are practically limited by the horizon, networks will be accomplished by relay stations connecting large cities. General Electric set up the first network five years ago, and has developed new tubes that make relaying practical. G-E stations WRGB, since 1939, has been a laboratory for engineering and programming.
Q. What is G.E.’s part in television?
A. Back in 1923, a General Electric engineer, Dr. E.F.W. Alexanderson, gave the first public demonstration. Before the war, G.E. was manufacturing both television transmitters and home receivers. It will again build both after Victory. Should you visit Schenectady, you are invited to WRGB’s studio to see a television show put on the air.
TELEVISION, another example of G-E research
Developments by General Electric scientists and engineers, working for our armed forces on land and sea and in the air, are helping to bring Victory sooner. Their work in such new fields as electronics, of which television is an example, will help to bring you new products and services in peacetime years to follow. General Electric Company, Schenectady, N.Y.
Hear the General Electric radio program: “The G-E All-girl Orchestra,” Sunday 10 p.m. EWT, NBC – “The World Today” news, every weekday 6:45 p.m. EWT, CBS.
An advertisement from The New York Times about new radios – well, not-so-new radios! – from 1942, by the Stromberg-Carlson Company, listing radio retailers in the New York Metropolitan area, northern New Jersey, and Connecticut.
(Who?)
The company was founded in 1904, and after being purchased by the Home Telephone Company in 1904, relocated from Chicago to Rochester, New York, where it became, “…a major manufacture of consumer electronics including home telephones, radio receivers and, after World War II, television sets.” Notably – at least in terms of this blog – the company produced the BC-348 communications receiver, which was used in WW II Army Air Force multi-engine transports and bombers.
The company was purchased by General Dynamics in 1955, and by 1980, sold by them in several components.
The full text of the ad is given below.
The acronym “OPA” refers to the Office of Price Administration, an agency of the Federal Government established in August of 1941, within the Office for Emergency Management. The OPA became an independent agency in January of 1942, and, “…had the power to place ceilings on all prices except agricultural commodities, and to ration scarce supplies of other items, including tires, automobiles, shoes, nylon, sugar, gasoline, fuel oil, coffee, meats and processed foods. At the peak, almost 90% of retail food prices were frozen. It could also authorize subsidies for production of some of those commodities.”
 Manufacture of new radios stopped April 22nd, 1942. Early completion of production brought about by 100% conversion to war orders has again made available a variety of our Radios and Radio-Phonographs.
Manufacture of new radios stopped April 22nd, 1942. Early completion of production brought about by 100% conversion to war orders has again made available a variety of our Radios and Radio-Phonographs.
If you are thinking of a new instrument to last you beyond the duration, we suggest you make your purchase soon. For when the current stock of new radios is gone, there will be no more until the war is won.
And you know that, for a long-term investment in good music at its best, you will find “There is nothing finer than a Stromberg-Carlson!”
Visit your nearest dealer listed below, where you will find most models on display, at OPA prices.
Manhattan, Bronx, Westchester, Brooklyn, Long Island, New Jersey, Connecticut
COMPLETE LINE ON DEMONSTRATION
Gross Distributors, Inc., 570 Lexington, Avenue, New York City
Representative for New York and New England
Write for free booklet “Facts about FM”
References
Office of Price Administration, at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Office_of_Price_Administration
Stromberg-Carlson, at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stromberg-Carlson
From July 10, 1945, here’s an advertisement by General Electric promoting and introducing “PLASTICS”.
The advertisement, divided into six sections – each with an emblematic illustration – describes the use of plastic in three contexts: Military: The M-51 fuse; The home: kitchen utensils; Industry and machinery: gears; The military once again: the triple-cluster aerial bazooka as used by USAAF P-47s and P-51s, and, binoculars. The ad then concludes with a section about the design and development of plastic.
Though the first genuinely synthetic polymer had existed for some time (Bakelite, created by Leo Bakeland in 1907), only by the 40s and 50s did mass production of plastic actually commence.
The war was winding down, victory was obvious, and GE was thinking of the future.
The full text is presented below…
 26,000,000 fuses. At the tip of this trench mortar is the M-51 fuse – most difficult mass production job ever done in plastics. Sixty-seven different operations check its perfection. Design was completed and mold started by G.E. the day before Pearl Harbor. Why was General Electric picked for this job?
26,000,000 fuses. At the tip of this trench mortar is the M-51 fuse – most difficult mass production job ever done in plastics. Sixty-seven different operations check its perfection. Design was completed and mold started by G.E. the day before Pearl Harbor. Why was General Electric picked for this job?
You’ll find the right answer in your own kitchen. The handle on your coffee maker, the case on the kitchen clock, the light switch on the wall – chances are these are G-E plastics. For General Electric has molded more plastic products than anybody else. And some you’d never guess. For example…
Cloth that wears like steel. Steel against steel is noisy. Wears fast. Imagine, then, a gear made of cloth – packed in layers, impregnated with resin, pressed under heat. Oddly enough, G-E engineers who discovered this found that for certain uses such gears were not only quieter, but actually outwore steel.
Would plastic bazookas blow up? The first hundred plastics tried failed. Then G.E. laminated a rare paper with a special resin. The plastic tube stood the shock of repeated firings, was non-inflammable. Now many planes carry these rocket launchers. G.E.’s 1400 presses turn out everything from electronic equipment housings to submarine parts.
Salt-water-proof binoculars are new. And won’t mildew in the tropics. General Electric worked these out with the U.S. Naval Observatory and specialists in optics. Plastics were combined with metal, and, to make shrinkage the same, a new metal alloy was developed. The lenses are universal focus, specially treated for night vision.
How do plastics get born? Designers say what shape, how heavy or light, soft or hard. Engineers design special machinery. Chemists then invent the plastic to fit the need. Finally, a factory can go to work. In war or peace, General Electric research and engineering count in plastics, too. General Electric Company, Schenectady, New York.
Hear the G-E radio programs: The G-E All-girl Orchestra, Sunday 10 p.m. EWT, NBC – The World News, Monday through Friday 6:45 p.m. EWT, CBS – the G-E House Party, Monday through Friday, 4 p.m. EWT, CBS.
Reference
Thompson, Richard C., Swan, Shanna H., Moore, Charles J., and vom Saal, Frederick S., Our Plastic Age, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, B, V 364, July 27, 2009.
This advertisement is particularly eye-catching in its use of light and dark, which visually symbolizes its message: An organization, operating regardless of day or night, producing vitally needed products for the military. The company? Reeves Sound Laboratories.
Located at 215 East 91st Street in Manhattan (unfortunately, there does not seem to be a Google street view of the address), the company, founded by Hazard E. Reeves, was a division of Reeves-Ely Laboratories, and conducted research into advanced gunfire control systems and computers, radar and tracking systems, guided missile controls, aircraft control instruments, flight trainers and aerodynamical computers, precision instruments, servo mechanisms, and, sound recording systems. By 1956, the company merged into the Dynamics Corporation of America.
AND OVER BERLIN – BOMBER CREWS ARE USING A PRODUCT MADE JUST OFF BROADWAY
Previously, the cutting of crystal oscillators had been an art known to only a few technicians. But then these New Yorkers pitched in: Debutantes, dancing teachers, actors, stenographers, artists, clerks, butcher boys, beauticians, models and others joined hands with housewives to show what they could do when a war industry came to Times Square.
Over a thousand workers (mostly women) came from the five boroughs and the suburbs. Everyone started from scratch. Management and workers were unskilled at the start. They learned the job together under the guidance of the United States Army Signal Corps experts. Production processes were studied and broken down into the simplest possible operations. X-Ray equipment and other highly scientific apparatus were brought in to help.
In the first month, only a few crystal were produced. Now a year later, these people are turning out many more crystals than was believed possible a year ago.
A production miracle? Perhaps. But maybe it’s because these people are Americans – because they’re New Yorkers…or because a large percentage of the employees have relatives doing the toughest job of all – in the Armed Service of their country.
These workers have done their work so well that they have been awarded the Army-Navy “E” which they accept with this pledge:
“I promise to wear this pin as a promise to every man in our Armed Services that, until this war is won, I will devote my full energies to the cause for which they are giving their lives.”
First to fly above Times Square, this pennant will give promise of even greater things in store for ’44.
For a fascinating glimpse into the Lab’s activities with a direct connection to the advertisement, watch the 1943 video Crystals Go To War, (at Jeff Quitney’s channel) – “narration by one of the research scientists of the U.S. Army Signal Corps” – produced for Reeves Sound Laboratories by Andre deLaVarre. The film is also available at Archiv.org.
References
Industrial Research Laboratories of the United States – Including Consulting Research Laboratories (Bulletin of the National Research Council) Number 113; July, 1946. Compiled by Callie Hull, with the assistance of Mary Timms and Lois Wilson.
Hazard E. Reeves, at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hazard_E._Reeves
Reeves Instrument Corporation, at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reeves_Instrument_Corporation
Here’s an advertisement from January 18, 1945 for a company that – refreshingly! – exists even today: American Car and Foundry.
Formed and incorporated in Jew Jersey in 1899, the firm is located today in Milton, Pennsylvania. According to the Wikipedia entry, the manufacturing facility, “…is capable of manufacturing railcars and all related railcar components. The plant is capable of producing pressure vessels in sizes 18,000–61,000 gwc, including propane tanks, compressed gas storage, LPG storage, and all related components, including heads. The plant, covering 48 acres, provides 500,000 square feet of covered work area and seven miles of storage tracks.”
(How nice to know that something physical is still manufactured in the United States!)
Regarding the advertisement itself, the illustration is a very nice example of graphic art. Every major product manufactured by the company is presented, from (primarily) railroad cars, to naval vessels, to shells or bombs, and (it looks like…) tires, with every manufactured item “leading” back to a point on a simplified map showing the location of its relevant manufacturing facility. Above all, the use of light and shadow is quite striking.
The full text of the ad is presented below.
 In the service of AMERICA … and its RAILROADS
In the service of AMERICA … and its RAILROADS
AWARE of the magnificent job American Railroads are doing, and aware too that THE WAR IS NOT YET OVER – A.C.F. pauses for an instant in its immense task of producing materials for our armed forces – Pauses to SALUTE THE RAILROADS, their men in maintenance, operations, and those who man the trains. They are truly a potent factor in the successful waging of war.
A.C.F., with sleeves rolled up, has well-laid plans for the future, for the wonder trains of tomorrow, and the facilities and “know how” that will help American’s Railroads attract and hold traffic.
IN WAR A.C.F. produces Combat Tanks, Shells, Bombs, Tractors, Landing Mats, Minesweepers, Net Tenders and many implements of War for our Army and Navy.
IN PEACE A.C.F. will again lead in Production of – Railway Passenger Cars, Streamliners, Freight Cars, Subway Cars, Mine Cars and a variety of other Products.
Whatever A.C.F. Builds – It is Known to Build Well!
References
ACF Industries, LLC, at http://acfindustries.com/
American Car and Foundry, at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_Car_and_Foundry_Company
American Car and Foundry has survived; other corporations have not.
Among them, Pennsylvania Railroad.
The advertisement below – from January 15, 1945 – has a title that proved to be as optimistic as it was ironic, for after merging with New York Central Railroad in 1968, the resulting firm, the Penn Central Transportation Company, filed for bankruptcy in 1970.
The advertisement combines three elements to produce a striking image. On the left, symbolizing the future, new designs for railroad cars are displayed on a unfurled blueprint, against which are placed a T-square and right triangle. Translucent images of those “future” railroad cards are shown below. On the right, a fleet of existing freight and railroad cars, en route from “a city” and “factory” pass by a suburban rail station. In the background, stylized images of that city and factory are set against the horizon of a cloudless sky, surrounded by farmland. Above all is the emblem of the Pennsylvania Railroad.
 Though “this” example of the advertisement was published in The New York Times, certainly the original advertisement was in color, and probably intended for publication in magazines. Here’s an example of the original ad, from Pinterest:
Though “this” example of the advertisement was published in The New York Times, certainly the original advertisement was in color, and probably intended for publication in magazines. Here’s an example of the original ad, from Pinterest:
Here is the full text of the advertisement:
EYES ON TOMORROW
On drawing board and blueprint, in research laboratory and on testing machines you will find the shape of things-to-come in railroading.
We know the American public expects great things – new, modern trains; daring designs; exciting and novel innovations; new power; new speed; new riding qualities; new comforts and luxuries; new services and ideas in travel, in shipping … in a word, transportation values beyond anything known or experienced before.
In its planning, the Pennsylvania Railroad has these things in mind – for it is a tradition of this railroad to look ahead, and apply its research to finding new ways to serve the traveling and shipping public better!
★ 50,757 entered the Armed Forces ☆ 532 have given their lives for their Country
BUY UNITED STATES WAR BONDS AND STAMPS
That the advertisement was created during the Second World War is strikingly evident by one particular facet of the text: The number of Pennsylvania Railroad Employees who died on WW II military service. Though listed as 532, the actual number is more than twice as many: 1,307. The discrepancy was likely attributable to the fact that the advertisement was created before the war actually ended, and thus, well before the status of all casualties (especially those missing in action) was verified.
The 1,307 men are memorialized at Philadelphia’s 30th Street Station, in the form of a bronze sculpture showing the Archangel Michael lifting a fallen soldier out of the “flames of war”. The sculpture is set atop a four-sided black granite base, upon the sides of which are bronze plaques listing the soldiers’ names in alphabetical order, and, bearing symbols of the four branches of the armed forces.
Designed by Walter Hancock and unveiled in 1952, the sculpture is – even decades later – extraordinarily striking.
References
Pennsylvania Railroad, at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pennsylvania_Railroad
Pennsylvania Railroad World War II Memorial, at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pennsylvania_Railroad_World_War_II_Memorial
The prior post – covering photographs of the loss of the 42nd Bomb Squadron B-24 Liberator Dogpatch Express – ended on an uncertain note.
Both the Missing Air Crew Report and 42nd Bomb Squadron history present detailed accounts of the bomber’s loss. However, both documents are ambiguous about the specific cause of the aircraft’s loss, let alone what ultimately befell the few survivors of the plane’s ditching. Given that PBY rescue planes later reported neither survivors nor wreckage at the site of the Express’ ditching, the Squadron history suggested that any surviving crewmen may have been captured by the Japanese, or, they were killed by strafing Zeros.
There, the matter seemed to rest.
A search for additional information about the “Grey Geese” and Dogpatch Express yielded a new and rather unexpected account, which appears in the 1996 book 11th Bomb Group (H): The Grey Geese. There, some fifty-three years after the Taroa bombing mission of December 21 1943, veteran Jesse Stay – whose account of the loss of Dogpatch Express appears in MACR 1423 – presented an account of the event that fully and sadly clarifies what happened to the plane and crew.
Mr. Stay’s account – presumably written in the 1990s – is presented below.
It turns out that the plane was initially struck by anti-aircraft fire in the cockpit (oddly, not mentioned in either the MACR or squadron history), to the extent that Lt. Smith was forced to fly, and ditch, the aircraft unassisted. As for the survivors, the impression is given that they were strafed in the water by more than one Zero (again, not mentioned in the MACR or squadron history).
Notably, Mr. Stay wrote that the pilot of the Express, 1 Lt. George W. Smith, was filling in for the crew’s regular pilot, Lt. Thompson, who was wounded over Wake on July 24, 1943. This may explain an aspect of the photo of the Express’ crew, which appears both below, and in the prior blog post: The fact that a member of the plane’s crew – probably having been wounded – is seated in a wheelchair.
Could this man be Lt. Thompson?
 THE DOGPATCH EXPRESS AND THE BELLE OF TEXAS
THE DOGPATCH EXPRESS AND THE BELLE OF TEXAS
By Jesse Stay
A mission out of Funafuti is worth remembering. It was on Dec. 20, 1943. We were bombing Maloelap Island in the Marshall group. This was shortly after we had taken Tarawa and the Japanese were able to bomb Tarawa from Maloelap. Our squadron was scheduled to bomb the target in three flights of three planes each. I was leading the second flight. We were to bomb from about 12 thousand feet at approximately noon.
My right wing man was scheduled to be Les Scholar but he became ill and was scratched from the mission. With Les out of the formation, that left only two planes in my flight. The pilot of the second plane, Lt. Charlie Pratte, flying the “Belle of Texas,” also got sick and began to throw up right after take-off. He had a capable co-pilot, however, so they decided to continue the mission.
When we reached Maloelap, the first flight went over the target and dropped their bombs without too much difficulty. We learned later that a 90 mm shell had come up through the open bomb bay doors, through another open door into the back of the airplane and out through the roof of the plane, directly over the heads of the two waist gunners and exploded harmlessly several hundred feet above the plane.
I then led my flight of two planes across the target and we dropped our bombs. As we cleared the target, we were picked up by a dozen or so Zeros so we tried to close up with the first flight for our mutual protection. Our tail gunner then told us that the “Dogpatch Express,” flown by Lt. Smith in the third flight, had been badly hit by anti-aircraft fire and was falling behind the formation. The Zeros were on him like a pack of wolves.
I made a 360 turn with my flight and got in formation with the stricken airplane to try to give him some protection. At the same time, the leader of the first flight, Lt. Warren Sands, made a turn in the other direction and brought his formation up on the other wing of the plane that had been hit.
Apparently an anti-aircraft shell had exploded inside the cockpit, killing the co-pilot and the top turret gunner. There was blood all over the cockpit. Two engines on the right side were out, one of which was on fire. We fought Zeros and tried to encourage Lt. Smith at the same time. His crewmen were throwing out all extra weight in the hopes that the plane could fly on the two left engines. It was too much for the pilot to handle, however, and he finally ditched the plane about 90 miles south of Maloelap.
The plane sand in about 30 seconds. It appeared to us that some of the crew were in the water so we dropped our life rafts as close as we could to the crash site. The other flights had left by this time because of lack of fuel. I stayed around for a few more minutes circling below the clouds at low level, until the Zeros left to return to Maloelap. They were machine gunning the debris from the crash and any survivors. We were trying to discourage this with the few guns we had on our two plans. We were still under attack by the Zeros and there were times on this mission when I could see a hail of tracers coming between my airplane and the “Bell of Texas” on my wing.
Finally Charlie Pratte also had to leave and headed for Tarawa to re-fuel. He had over 300 holes in his airplane but didn’t have one man wounded. On one pass the Japanese machine guns had stitched holes the length of his fuselage and had blown up the oxygen tanks which had knocked down the two waist gunners in time for the machine gun bullets to pass through the fuselage where they had been standing. I later found out that his hydraulic system was also shot out and he landed at the new strip at Tarawa with parachutes tied to the waist and tail guns and which the crewmen deployed as they touched down to slow the airplane because they had no brakes. We had talked about this possibility before but the crew of the “Belle of Texas” received a commendation from General “Hap” Arnold, Chief of Staff of the Army Air Corps for making the first recorded parachute landing. This technique is now used for many of our high speed aircraft and on the space shuttle to slow down on landing.
We called for Dumbo rescue but Smitty and the “Dogpatch Express” were never found. There were no survivors. Lt. Smith was flying on this mission with the crew of Lt. Thompson who had been wounded over Wake Island on July 24, 1943.
Lt. Pratte had his crew were lost on January 22, 1944 on a low level mine laying mission out of Guam over Chichi Jima.
I landed on Tarawa on the old, bomb pocked strip a little later and after taking on 1,000 gallons of fuel from give gallon cans, we took off for Funafuti, a small atoll about six hundred miles to the south. We didn’t want to waste fuel climbing to the south, so we decided to stay below the clouds. For this reason we couldn’t get a fix on the stars and by this time it was dark so that we couldn’t measure our wind drift from the waves below us. We navigated by dead reckoning for what we estimated to be six hundred miles and then started a square search for our little island. On our second right angle turn of our square search we saw some faint lights a few miles away and we were soon back on the ground after being gone for 19 hours with 17 hours in the air. We didn’t have a single hole in our airplane when we examined it after landing.
Reference
May, Bob; Parker, Bud; Gudenschwager, Phil, 11th Bomb Group (H): The Grey Geese, Turner Publishing Company, Paducah, Ky., 1996.
Previously, I presented photographs from two Missing Air Crew Reports (MACRs) covering the loss of two 416th Bomb Group A-20 Havoc attack-bombers over France in 1944. That post concluded on an “upbeat” note: The six aviators from both planes safely parachuted and survived the war as POWs, eventually returning to the United States.
The circumstances surrounding “this” post – covering the loss of an 11th Bomb Group (…”Gray Geese”…) B-24 Liberator in the Central Pacific Ocean in late 1943 are, sadly, very different. Though at least some members of the plane’s crew initially survived the ditching of their plane in the Central Pacific, they were never seen again.
In that sense, this Missing Air Crew Report and the two photographs within it epitomize – in a manner far more powerful than words – the nature of the Pacific air war, some seven decades ago.
____________________
The aircraft in question, B-24D 41-24214 (Dogpatch Express) was one of a group of eight B-24s of the 42nd Bomb Squadron, 11th Bomb Group, 7th Air Force, which staged through Nanomea (the northwestern-most atoll in the Polynesian nation of Tuvalu) for a strike against Taroa Island (not to be confused with Tarawa, in the Gilbert Islands!), in the Maloelap Atoll of the Marshall Islands, on December 21, 1943.
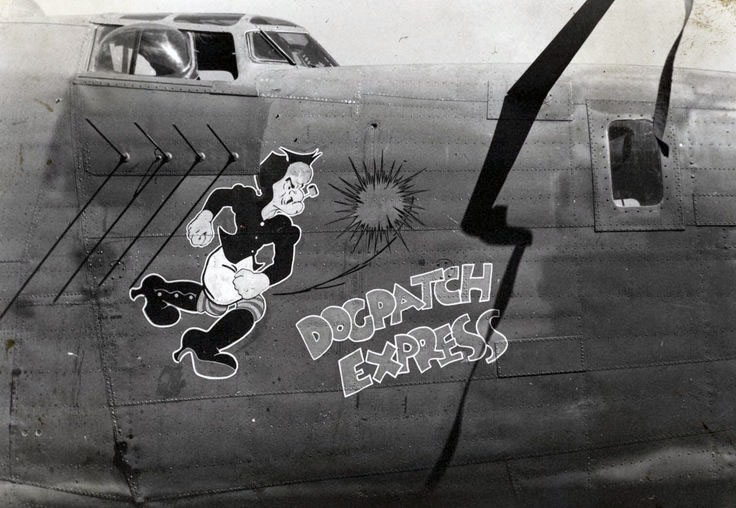
Here is a superb photo of Dogpatch Express’ nose art, from Pinterest (via Hawaii.gov):
 Here’s another view of the plane (the crewmen are unidentified) appropriately from B-24 Best Web:
Here’s another view of the plane (the crewmen are unidentified) appropriately from B-24 Best Web:

____________________
What happened?
The MACR (# 1423) describes the sequence of events surrounding the loss of the bomber in very great detail, an aspect of MACRs covering 7th Air Force B-24 losses which seems to have been quite consistent.
After the squadron’s bombing run on Taroa, Lt. Smith’s plane was observed to lag behind the other seven bombers, though the specific cause is not delineated in either the MACR or squadron history. Five other B-24s turned back to provide protection for the Express, with one escorting pilot, Captain Jesse Stay (whose account is presented below) maintaining radio contact with Lt. Smith. Having already lost his #4 engine, the Express’ #3 engine soon began emitting smoke, upon which 252nd Kokutai Zeros and Hamps (assigned to the defense of Taroa, as described at Pacific Wrecks) – which had been attacking the formation from the time it left the target – began to especially concentrate their fire upon Smith’s aircraft.
Heavily damaged, with its #4 engine out and #3 engine smoking, Lt. Smith lost altitude, and, eventually ditched.
The Liberator broke in two immediately behind the flight deck, with part of the tail remaining afloat for several minutes. Throughout, three Zeros, which had probably expended their ammunition, remained in the area to observe the scene.
Taken together, the accounts of Captain Stay and Lt. Sands indicate that at least three – and possibly four – of the crew survived both the ditching and a strafing run by a solitary Zero. Two life rafts were deployed, and “water marker” (dye marker?) at the scene was visible from a distance of 10 to 12 miles.
So, at least some of the crew – presumably gunners in the rear of the aircraft – remained alive after the crash.
Later that day, upon the arrival of two PBYs at the location of the ditching (the time of their arrival is not listed and the naval squadron is unidentified) – nothing was found. To quote the squadron history: “It was later found that upon arriving at the spot, no trace was found of the survivors, and it is presumed that they either were strafed by returning Jap airplanes or taken prisoner.”
____________________
The accounts of Captain Stay and Lt. Sands are presented below verbatim, along with a summary of the mission from the records of the 42nd Bomb Squadron:
Captain Stay’s Account
My flight, consisting of myself and Lt. Pratte in A/P #156 followed Capt. Storm’s flight of three airplanes over the target on Taroa Island. We were followed by “C” flight in which Lt. Smith in A/P #214 was No. 2 man. We made our run and turned off to the left, increasing our power and diving to catch up with Capt. Storm’s “A” flight. We had been off of the target approximately 12-15 minutes when S/Sgt. Blackmore, my tail gunner called me to say that one A/P in “C” flight had become a straggler and was being attacked by several Zeros. As he told me this Lt. Sands in A/P #073, who was flying #2 position in “A” flight pulled out of formation and started a turn back. My flight of two ships turned with him and at the same time my Co-pilot informed Capt. Storm of the straggler. Lt. Sands fell in on Lt. Smith’s right wing and I took up a position on his left wing with Lt. Pratte flying on my left wing.
Shortly after this Capt. Storm and his remaining wing man, Lt. Perry in A/P #007 fell into our formation. At this time we noticed that the #4 engine on A/P #214 was feathered and he had many holes in the fuselage and emphennage of his A/P, and he was losing altitude fast. Approximately 3 minutes after we joined him in formation his no. 3 engine caught fire giving off a heavy white smoke.
I spoke to Lt. Smith over V.H.F. and suggested that he feather no. 3 engine and try to put cut the fire with his Lux System. Lt. Smith called back asking me to get Dumbo service for him and I acknowledged. Shortly after Lt. Smith feathered #3 engine and the fire was apparently extinguished. From the time that we had left the target we had been having a running fight with from 15 to 20 Zeros. When Lt. Smith’s #3 engine began to smoke the Zeros began to press their attack and from 7 to 8 overhead passes were made at the formation before Lt. Smith landed his ship in the water. The Zero pilots made excellent use of the sun and they seemed very experienced in this type of attack.
Lt. Smith had been losing altitude rapidly and when he was at about 3,000 ft. he started #3 engine again and it immediately began to smoke again. We dropped down through a .4 cumulus cloud cover and our formation circled through a hole to 1000 ft. to watch his landing. At this time there were still four Zeros in the air but they were apparently out of ammunition because they made no more passes.
Lt. Smith landed in the water at 13:45 L.W.T. at a position of 08 04 N and 172 33 E. The ship broke in two and the nose appeared to go down leaving the trailing edge of the wing and very little of the bomb bay afloat. The whole ship was under water in approximately 3 minutes. We observed at this time one life raft with one man lying prone across it. The rest of the formation left for their base and Lt. Sands, Lt. Pratte and myself circled the scene for cover and to give what aid we could. Three Zeros were still in the area but appeared to be only observing the crash. Our top gunner was only able to fire a few shots at any of them.
Lt. Sands dove in low over the raft and dropped a life raft then we dove in and dropped a box of emergency rations. Both the raft and the rations remained intact and afloat. We called for Life Guard service on command voice on 6210 K.C. giving our distance of 90 miles and our course of 120° M from the target.
The Zeros left and we climbed above the clouds and Lt. Pulliam took a sun shot over the raft and confirmed our position. At the same time my radio operator was calling first Tarawa, then Makin, then Apamama but receiving no answer from any of them he again called Tarawa and sent through a request for Dumbo Service. Our three planes left the scene for Tarawa and after we had been on course for approximately 10 minutes the men in the back of my A/P reported seeing what they thought was a submarine wake behind us. I turned around and headed back to the raft hoping to be able to assist the Submarine but on approaching the life raft we were able to see the water marker for from 10 to 12 miles from 1000 ft.
As we dove over the scene to fifty feet we saw that there were two rafts inflated and three men ware in one and possibly one on the other. We set our liaison up to transmit on 6210 and called for Life Guard Service again. We left the scene finally at 1434 L.W.T. and landed at Tarawa to refuel where we learned that two PBYs had been sent out 2 hours before.
Captain Jesse E. Stay
Lt. Sands’ Account
I was flying A/P # 073 in the Number 3 position of “A” Flight. We had left the target about five minutes when the tail gunner called and said there was a B-24 smoking and losing altitude and was alone. I told my crew that we were going to make a 90° turn so I could get a look at it. When I observed the conditions under which Lt. Smith was placed I continued my turn and went back to get in formation with him. We pulled in on his right wing as that was the side that about 10 Zekes were making overhead passes at the crippled plane. We had been in formation with Lt. Smith about three or four minutes when the four other planes pulled into formation on his left wing. We continued to escort him until he landed in the water at about 13:45 L.W.T.
The plane appeared to break in two just back of the flight deck. The entire plane with the exception of the tail surfaces sank almost immediately. The tail surfaces floated for about four minutes. One man was definitely seen to be laying across a partly inflated, overturned life-raft with possibly one other person in the water. I ordered my crew to get a life raft ready to throw overboard which was done as we passed over at a minimum altitude.
One Zeke was seen to make a strafing attack at the spot where the plane sank. The Zeke then left the area. We circled for another ten minutes, and seeing no more Zekes, we departed for Tarawa. My radio operator immediately sent out a position report of the crashed plane which was unanswered.
1 Lt. Warren H. Sands
42nd Bomb Squadron History
TAROA MISSION * 20 December 1943
Lt. Kerr in 143, Captain Storm in 155, Lt. Gall in 100, Lt. Perr (431st) in 007, Lt. Schmidt in 838m Lt. Stay in 960, Lt. Sands in 073, Lt. Smith in 214, and Lt. Pratte in 156, staged through Nonomea for a strike against Taroa on Maloelap Atoll. Each airplane carried 6 x 500 GO bombs. Interception began as the airplanes pulled away from an AA spattered bomb run, with 20 – 30 Zekes and Hamps rising to the attack.
AA began as the airplanes neared the island, in some cases not reported as occurring until the run had started, with a majority of the bombs landing in or near the target area. Lt. Gall did not reach the target due to malfunction. It was on this mission that Lt. Smith had two engines shot out either by AA or cannon fire, and found it necessary to make a water landing about 75 miles from Taroa. Covered by other elements of the flight, he made what was described as “an excellent” water landing, from which at least four men were seen to leave the badly damaged airplane and crawl onto two rafts. Captain Stay had, prior to the crash, radioed to both Dumbo and Lifeguard to come in, and this was later found to have reached both agencies through other intercepting mediums as well as the original call. It was later found that upon arriving at the spot, no trace was found of the survivors, and it is presumed that they either were strafed by returning Jap airplanes or taken prisoner.
Several Jap interceptors were knocked off on this mission, by Sergeant Kernyat of Sands crew, Sgt. Brannan of Lt. Kerr’s, Sgt. Roth, Sgt. Ball, and S/Sgt. Tanner of Captains Stay’s crew. They were all confirmed…
____________________
To give you a better understanding of the setting and location of this incident, the following series of maps and illustrations show the location of the Marshall Islands in general and Taroa in particular, the island’s appearance in 1943 (and 2017), as well as the location where Dogpatch Express was lost in relation to surrounding islands.
____________________
Here is a map of the Marshall Islands (from Wikimedia Commons) illustrated on a global view of the earth, centered on Polynesia.
The map below, from the Diercke International Atlas, shows Taroa Island (right center) and the other islands comprising the Maloelap Atoll.
This undated Air Force photograph shows the “Bombing of the Japanese Airfield on Taroa Islet [sic]…” The image is from the WW II U.S. Air Force Photo Collection at Fold3.com. (Image A42044 / 73717 AC)
Here’s a Google Earth satellite view of Taroa, circa 2017. The island’s miniscule size is evident by the distance scale (one thousand feet!) in the lower right corner of the image. Note the changes in the island’s shape that have ensued since World War Two, and, the still-visible remnant of one of the two runways.
This Google map shows the location of Taroa (via the red pointer), relative to surrounding islands. Obvious (in reality, not-so-obvious) is the fact that the Maloelap Atoll and Taroa are “invisible” at the scale of this map.
This map, generated by entering latitude and longitude coordinates in Google Earth, shows the location where Dogpatch Express was ditched (denoted by the red pointer). Akin to above, at this scale, Maloelap and Taroa do not appear.
This map shows the location of Nanomea Island (red pointer once more) relative to the Marshalls. Akin to the above map views, Nanomea is so small as to be “invisible”
The plane was lost.
Ten men were lost.
Who were they?
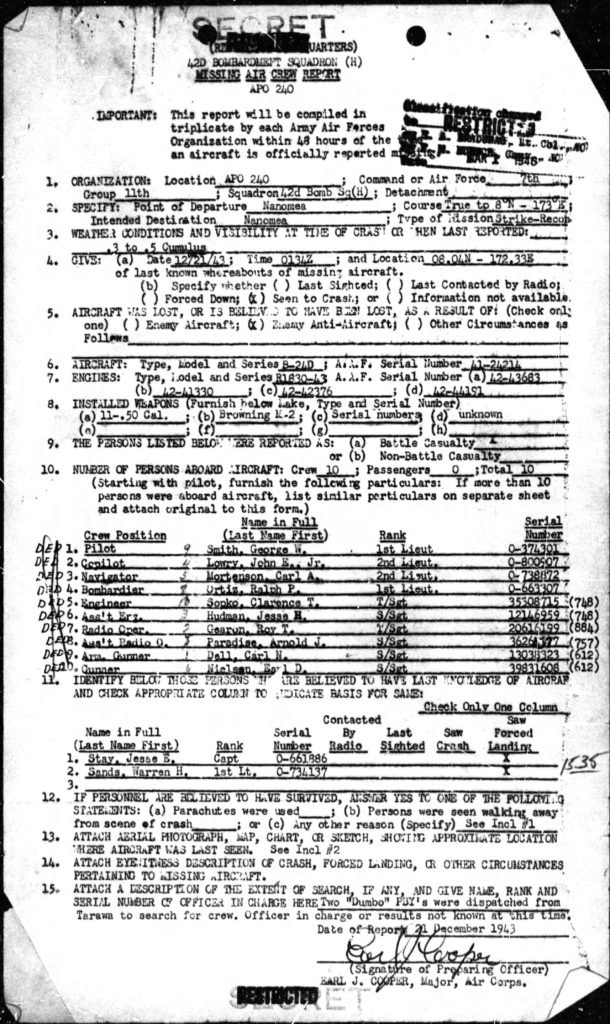
Typical for MACRs, Report 1423 gives the names of the plane’s crewmen, their crew positions, and, their serial numbers. However, the Report does not contain any “contact” information; the names and residential address of next-of-kin. If you were to go by the MACR alone, the men would be, in a sense, “anonymous”: names, ranks, serial numbers, and nothing more.
 However, there is one set of records in the National Archives that gives these men fuller identities.
However, there is one set of records in the National Archives that gives these men fuller identities.
This information is present in Records Group 165, in the “Bureau of Public Relations Press Branch” releases covering military casualties (specifically Missing in Action, Killed in Action, Wounded in Action), which were issued throughout the war to the news media by the War Department.
Within these press releases, casualties are listed by theater of war (Europe, Mediterranean, Pacific, etc.), with mens’ names listed alphabetically within each category. The name of a casualty was usually (usually) released approximately one month subsequent to the calendar date on which he was killed, wounded, or missing. The predictably of this time-frame is a very reliable way (at least, through the late spring of 1944) to identify the year and month when the press release listing a serviceman’s name, his next-of-kin, and emergency address, was released to the news media.
(Maybe more about this in a future post?)
Given that Lt. Smith’s crew was lost in late December of 1943, it was assumed that their names could be found in Press releases issued in late January of 1944. Research in RG 165 verified this: The men’s names appeared in Casualty Lists issued on January 21, 22, and 24, and (one man) February 9, of 1944.
____________________
The crew’s names are other relevant information are presented below, along with (in parenthesis) the calendar date of the relevant Press release.
They were:
Pilot Smith, George W. 1 Lt. 0-374301 (1/22/44)
Mrs. Ida R. Smith (mother), Prairieton, In.
Co-Pilot Lowry, John E., Jr. 2 Lt. 0-800907 (1/21/44)
Mrs. Margaret E. Lowry, Jr. (wife), Spring St., Smyrna, Ga.
Navigator Mortenson, Carl A. 2 Lt. 0-738872 (1/22/44)
Mr. Harry Walter Mortenson (brother), 1380 Riverside Drive, Lakewood, Oh.
Bombardier Ortiz, Ralph P. 1 Lt. 0-663307 (1/22/44)
Mr. Daniel C. Ortiz (father), 603 Agua Fria, Santa Fe, N.M.
Flight Engineer Sopko, Clarence T. T/Sgt. 35308715 1/22/20 (1/22/44)
Mrs. Mary S. Sopko (mother), 2138 West 26th St., Cleveland, Oh.
Memorial Tombstone – at Ohio Western Reserve National Cemetery – Section M, Plot 6 (Photo by Douglas King)
Radio Operator Gearon, Roy T. T/Sgt. 20616199 (1/21/44)
Mrs. Catherine Ann Gearon (mother), 5464 Woodlawn, Chicago, Il.
Crew Picture and related information from Patrick Maher (Second Cousin) (See below.)
Gunner Hudman, Jesse Harvey S/Sgt. 12146959 1918 (1/21/44)
Mrs. Florence L. Hudman (wife), 10 Marble Place, Ossining, N.Y.
Mrs. Carrie Hudman (mother), Gilbert Park, N.Y.
Memorial Tombstone – at Dale Cemetery, Ossining, N.Y. (photo by Jean Sutherland)
Notices about Sgt. Hudman appeared in the Citizen-Register, of Ossining, N.Y., on May 22 and 25, 1946, concerning a memorial service that was held in his behalf on May 19 of that year.
 Gunner Paradise, Arnold J. S/Sgt. 36264577 (1/21/44)
Gunner Paradise, Arnold J. S/Sgt. 36264577 (1/21/44)
Mrs. Fern Paradise (mother), Garden Acres, Chippewa Falls, Wi.
WW II Memorial – June Havel (sister)
Gunner Dell, Carl N. S/Sgt. 13038323 4/19/20 (2/9/44)
Mr. William J. Dell (father), Route 1, Middle Road, Pittsburgh, Pa.
Memorial Tombstone at Saint Mary’s Cemetery, Pittsburgh, Pa. (Photo by “Genealogy-Detective”)
Gunner Nielsen, Earl Dewayne S/Sgt. 39831608 7/29/21 (1/21/44)
Mrs. Vera P. Nielsen (mother), Cleveland, Id.
Memorial Tombstone at Cleveland Cemetery, Franklin County, Id. (Photo by Bill E. Doman)
All the crewmen are memorialized in the Courts of the Missing (Court 7), at the Honolulu Memorial, in the National Memorial Cemetery of the Pacific, at Honolulu, Hawaii.
Remarkably, there is a photograph of this crew…
Mr. Patrick Maher, a second cousin of T/Sgt. Roy Gearon, has posted a picture of the crew at the Memorial Page for his relative at FindAGrave.com, with the message, “We are 2nd cousins Roy. Know you were remembered then and still by your family with a proud military tradition. May you and your crew forever rest in peace at the bottom of the ocean. Your last mission was accomplished Sir. Sorry on behalf of your government for your case and many like it. Your death date was December 21, 1943 not 1946. Silver Star recipient. Rest in Peace Sir.”
 Mr. Maher’s entry also includes a close-up image of the final moments of Dogpatch Express, identical to one of the photographs in the MACR below.
Mr. Maher’s entry also includes a close-up image of the final moments of Dogpatch Express, identical to one of the photographs in the MACR below.
____________________
The photos?
Unlike the images for the A-20s, these two photos are unattached to the documents in the MACR; they’re “loose” in the file. Here they are:
Here’s the “first” image. This shows Dogpatch Express heading back – well, trying to head back – to Nanomea, showing Lt. Sand’s B-24 to the right and slightly above Lt. Smith’s aircraft. This may be the point at which – as described by Capt. Stay – the squadron dropped to an altitude of 3,000 feet, upon which the Express’ #3 engine emitted smoke when it was restarted.
This is a 2,400 dpi crop of the above photo. The damage to Dogpatch Express is obvious. The #4 engine has been feathered, and there’s a large hole in the starboard rudder. Close examination shows that the ball turret has been rotated downwards and retracted into the fuselage, while in the dorsal turret – rotated to the rear – the guns have been elevated to 70-80 degrees. The trail of smoke – thick smoke; dense smoke; white smoke – emitted from the #3 engine is plainly evident.
Given that the direction of flight from Taroa to Nanomea was approximately south-southeast, by looking “into” this image – the viewer is looking west-southwest.
Beyond and below the aircraft, and into the indefinite horizon, there are clouds, water, and, more clouds and more water.
This picture shows the scene of Dogpatch Express’ ditching.
(Though this post doesn’t pertain to camouflage and markings, this image illustrates the Insignia Blue overpaint of the Insignia Red surround to the National Insignia, which had been a feature of the national insignia of American military aircraft between 28 June and 14 August 1943.)
Though intended as a historical record – for which it more than serves its purpose – this photograph – like the image above – is extremely evocative of the war over the Pacific: Distance. Water. Emptiness.
The point of the B-24’s impact – a trail of churned water perhaps several hundred feet long – is obvious. However, compared with the expanse of sea encompassed by the image and receding into the distance, the site is miniscule.
This is a 2,400 dpi crop of the above image. Though the resolution is too low to identify details, four objects can be seen floating at the top of the “ditching trail”. Captain Stay mentioned that the scene was visible up to 12 miles away, due to dye marker in the water. Is the gray patch of water in the upper left of the ditching site the dye marker?
The survivors – whoever they were – were never seen again.
The 42nd Bomb Squadron mission summary suggests two possibilities for their fate: They were strafed by Zero fighters during the interval between the departure of the other B-24s and the arrival of PBYs, or, they were captured by the Japanese, via naval vessels.
Given the location and circumstances under which the crew was lost, and, the passage of time, what ultimately happened to the few survivors will probably forever be unknown. There is a slight – (very slight?) – possibility that IDPFs filed for the crew may include more definitive information about their fate, but even those documents, I suppose, will be ambiguous as well.
What is not supposition was – and will always be – their bravery, and the bravery of many men like them.
____________________
A Brief Digression on Names and Numbers
Did the Army Air Force (or post-1947, the Air Force) ever complete statistical studies comparing the chances of survival for WW II USAAF bomber aircrews lost over the Pacific, to those for aviators lost in the European / Mediterranean Theatres of War? I don’t know!
I’ve attempted a brief comparison of that sort. Or, at least half of a comparison… This was based on an evaluation of statistics about 7th Air Force B-24 losses, with information derived from MACRs (my own review of those documents, extending over some years), and, miscellaneous references.
MACRs and other sources for losses of 7th Air Force B-24s (75 aircraft covered by “wartime” MACRs, 6 aircraft covered by post-war “fill-in” MACRs, and 11 B-24 losses mentioned by books and other sources) cover a total of 92 aircraft. (Doubtless there were other planes for which MACRs were never filed…)
Among those 92 B-24s, there was a total of 950 airmen, of whom there were 237 survivors and 713 fatalities. The 237 survivors represent 24% of the 950 crewmen. (There were no survivors from 51 planes, while entire crews survived among 5 of the 92 lost aircraft.)
In light of these statistics, and bearing in mind that these figures represent people, not simply “numbers” – I wonder if…it seems that…despite the greater aircraft losses incurred by the 8th and 15th Air Forces, as opposed to the 7th (and 13th, and 5th)…the chances of survival for an aircrew lost in the Pacific Theater of war were actually far lower than in Europe and the Mediterranean.
If so, I’d attribute this to the utterly different geography encompassed by and overflown in the Pacific, where combat missions by nature occurred over vast, near-featureless expanses of water; abruptly changing climatic conditions; the challenges inherent to locating downed airmen at sea, during both aerial and sea-borne searches; the lower chances of simple physical survival (aside from enemy activity) for those few aviators who may have been able to parachute onto land or sea; and last – but hardly insignificantly – the ethos of the Japanese regarding captured members of the Allied Air Forces. (Thirteen 7th Air Force B-24 crewmen survived the war as POWs of the Japanese.*)
So, to conclude (if there is a conclusion) let these photos stand as a reminder of those who didn’t return, and the very few who did.
____________________
Notes
For an essay on Taroa illustrated with stunningly beautiful contemporary photographs, visit The World War II Legacy of Taroa Island.
For a historical overview of Taroa, specifically focusing on the island during World War II and as a tourist destination (circa 1995), see the essay Dirk H.R. Spennemann (of the Institute of Land, Water and Society, at Charles Stuart University), at Taroa, Maloelap Atoll – A brief virtual tour through a Japanese airbase in the Marshall Islands.
* These POWs were:
ABEL, WILLIAM E. S/Sgt. 36440823 Gunner (Tail)
CARTWRIGHT, THOMAS C. 2 Lt. 0-831661 Pilot
EIFLER, HAROLD 2 Lt. 0-721673 Pilot
GARRETT, FRED F 1 Lt. 0-740163 Pilot
HRYSKANICH, PETER 2 Lt. 0-806683 Co-Pilot
MARTIN, WILLIAM R., JR 2 Lt. 0-2065804 Navigator
MINIERRE, LINCOLN S. T/Sgt. 11073217 Radio Operator
PHILLIPS, RUSSELL A. Capt. 0-726463 Pilot
SELLERS, CLYDE J. Sgt. 36871713 Gunner
SMITH, RICHARD M. 2 Lt. 0-692346 Navigator
STODDARD, LOREN A. Capt. 0-428873 Pilot
WALKER, ARTHUR JAMES Col. 0-022462 Pilot
ZAMPERINI, LOUIS S. 1 Lt. 0-663341 Bombardier
____________________
References
(Books)
Bell, Dana, Air Force Colors Volume 2 – ETO & MTO 1942-45, Squadron/Signal Publications, Carrollton, Tx., 1980.
Cleveland, W.M., Grey Geese Calling – Pacific Air War History of the 11th Bombardment Group (H) 1940-1945, 11th Bombardment Group Association Inc., Seffner, Fl., 1992.
Doll, Thomas E., Jackson, Berkley R., and Riley, William A., Navy Air Colors – United States Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard Aircraft Camouflage and Markings, Vol. 1 – 1911-1945, Squadron/Signal Publications, Carrollton, Tx., 1983.
Forman, Wallace R., B-24 Nose Art Name Directory, Specialty Press Publishers and Wholesalers, North Branch, Mn., 1996.
Rust, Kenn C., Seventh Air Force Story …In World War II, Historical Aviation Album, Temple City, Ca., 1979.
(Web Sites)
11th Bombardment Group History, at http://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/browse?type=subject&value=11th%20Bombardment%20Group%20(H)
At OAKTrust Digital Repository of Texas A&M University – Special Collections
http://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/
In connection with / related to biography of T/Sgt. Paul Fredrick Adler
42nd Bombardment Squadron (Heavy). Monthly Squadron Histories and Documents, 20 May 1943 – 5 March 1944
http://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/bitstream/handle/1969.1/90568/3%20History-42dBS-1943-44-Missions.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (On pages 89 of 104 of PDF.)
Dogpatch Express nose-art (Pinterest), at https://www.pinterest.com/pin/551268810615004024/
Dogpatch Express crew photo (B-24 Best Web), at http://www.b24bestweb.com/dogpatchexpress-v1
Dogpatch Express nose-art (B-24 Best Web), at http://www.b24bestweb.com/dogpatchexpress-v1-1.htm
Dogpatch Express nose-art (B-24 Best Web), at http://www.b24bestweb.com/dogpatchexpress-v1-2.htm
Marshall Islands (at Wikimedia Commons), at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marshall_Islands.
Nanomea Island (Wikipedia entry – listed as “Nanumea”), at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nanumea
Taroa Island (at Pacific Wrecks Database), at http://www.pacificwrecks.com/airfields/marshalls/taroa/index.html
Taroa Island (at Charles Stuart University), at http://marshall.csu.edu.au/Marshalls/html/japanese/Taroa/Taroa.html
The World War II Legacy of Taroa Island (at Nothing Unknown), at https://www.nothingunknown.com/content/2016/10/7/taroa-island
(United States National Archives)
Records Group 165 “War Department Special Staff Public Relations Division News Branch Press and Radio News Releases, 1921-1947” (arranged chronologically), at Stack Area 390, Row 40, Compartment 3, Shelf 6.